1. Bioelectric InStim inflammation treatment 2X a week for 40 minutes each for 3 weeks prior to stem cell injections. Reads inflammation and real time adjusts bioelectric signals to control anti-inflammatory cytokines release on demand. 2. Bioelectric stem cell recruiting and protein expression treatment in clinic for regeneration 2X a week for 20 to 40 minutes for 16 weeks. Includes SDF-1, IGF-1, HGF, EGF, PDGF, VEGF, HIF1a, eNOS, Activin, Follistatin, Tropoelastin, BMPs. 3. Adipose or bone marrow derived stem cell injections with may be suspended (where regulatory agencies accept) in a growth factor cocktail, amniotic fluid, PRF, nutrient hydrogel, selected exosomes, micro RNAs, selected alkaloids and joint matrix- 1X a month for 6 months or until joint is recovered. 4. PRP, PRF, Amniotic Fluid injections – 1X per month for 6 months or until joint is recovered. 5. @ home stimulation with portable microcurrent leg, knee, calf and foot electric stimulation microcurrent garments (joint wrap) – use everyday until recovery. 6. Electro-acupuncture with Dr. Y. King Liu patented knee brace wrap one treatment day a month for 6 to 18 months or until joint is recovered.
Treatment protocol will vary depending on regulatory constraints in certain countries and physician preference.
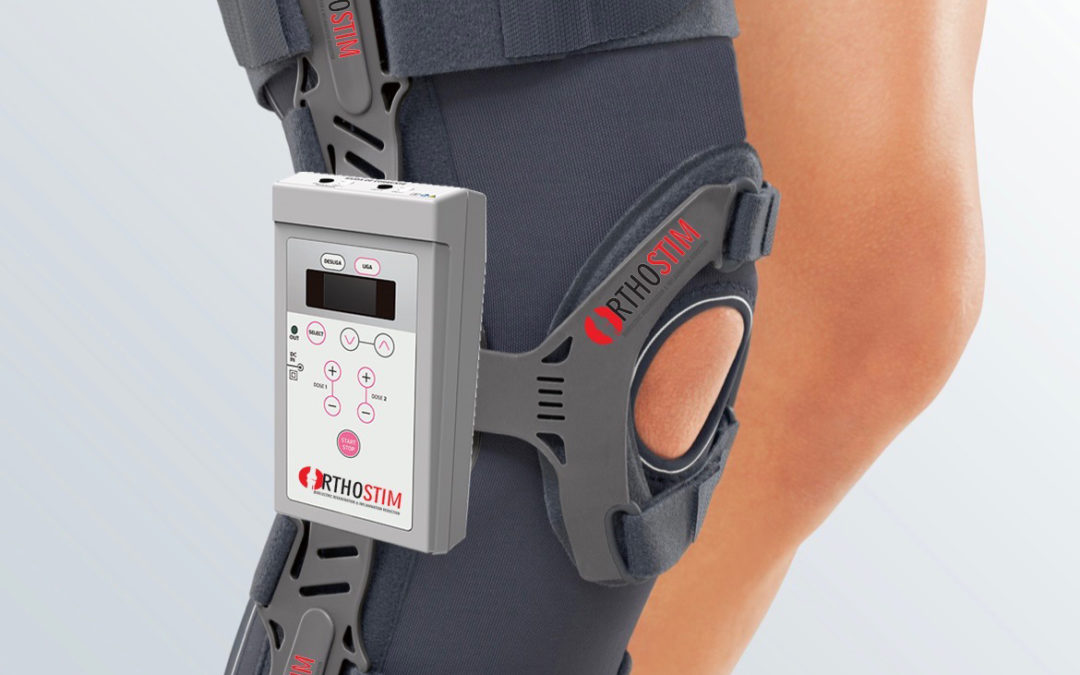
OrthoStim Bioelectric Knee Stimulation
Knee brace having electromagnetic stimulators for continual electro-acupunctural stimulation; in vivo and in situ tissue engineering
Publication number: 20170259058 Abstract: An acupuncture stimulation system comprises a skin overlaying component and a strap having hook-and-loop fastener material, the strap can be wrapped around the skin overlaying component to snugly secure a portion of the system. Type: Application Filed: May 22, 2017 Publication date: September 14, 2017 Inventor: Y. King Liu
Knee brace having three stimulators for continual electro-acupunctural stimulation; in vivo and in situ tissue engineering
Patent number: 9687376 Abstract: A knee brace for continual electro-acupuncture stimulation system comprises a first circuit having a first circuit having a first electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Heting (S 156)” and a second electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Bladder 40”, a second circuit having a third electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Spleen 10” and a fourth electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Hsiyen (S 145)”, and a third circuit having a fifth electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Stomach 34” and a sixth electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Stomach 35”. The first, third, and fifth electrodes are connected to a polarity of voltage, and the second, fourth, and sixth electrodes are connected to an opposite polarity of voltage, such that electric currents flow in a body of a patient to achieve analgesia, cartilage repair and regeneration in the knee joint. Type: Grant Filed: August 6, 2013 Date of Patent: June 27, 2017 Inventor: Y. King Liu
Knee brace for continual electro-acupunctural stimulation; in vivo and in situ tissue engineering
Patent number: 9629742 Abstract: A knee brace for continual electro-acupuncture stimulation system comprises: a first electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point Heting “(S 156)”; a second electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Spleen 10 ”; a third electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Stomach 34 ”; a fourth electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Hsiyen (S 145)”; a fifth electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Stomach 35 ”; a sixth electrode configured to electrically coupled to acupuncture point “Bladder 40 ”. The first, second, and third electrodes are connected to a polarity of voltage, and the fourth, fifth, and sixth electrodes are connected to an opposite polarity of voltage, such that electric currents flow in a body of a patient to achieve analgesia, cartilage repair and regeneration in the knee joint. Type: Grant Filed: December 24, 2012 Date of Patent: April 25, 2017 Inventor: Y. King Liu
Percutaneous continual electro-acupuncture stimulation for in vivo and in situ tissue engineering
Patent number: 9440069 Abstract: The invention includes an electro-acupuncture stimulation system for in vivo and in situ analgesia and tissue repair and regeneration. Electrodes, which can be acupuncture needles, are percutaneously implanted that deliver a pulsed electrical current that creates an electrical field, which envelopes the targeted tissue and restores cell-generating homeostasis to the affected tissue and thereby promotes analgesia and tissue re-growth in otherwise debilitated or deteriorating tissue. Methods and apparatuses are also disclosed that may include a needle locking system and acupuncture-needle assemblies for long-term in situ electrical stimulation. Type: Grant Filed: November 25, 2009 Date of Patent: September 13, 2016 Inventor: Y. King Liu